

In electrochemical series, the substances which are stronger reducing agents than hydrogen are placed above hydrogen in top half and have negative values of standard reduction potentials.
#ANODE CATHODE OXIDIZING AND REDUCING AGENT HOW TO#
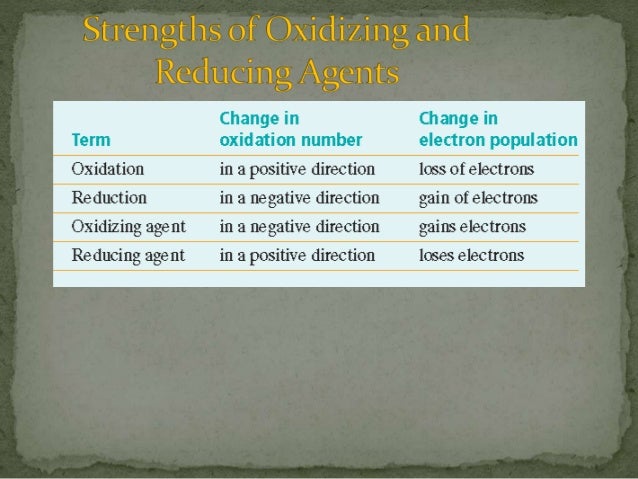
How to read electrochemical series ? It is simple and easy. The table below is showing how oxidizing and reducing substances are arranged in an electrochemical series. The text book definition of Electrochemical series is " it is an arrangement of elements in order of increasing reduction potential values"īy convention, the reduction potential or electrode potential is expressed as the potential acquired by a metal immersed in a solution of its ions of concentration 1 mole / liter at 25 degc and 1 atm pressure and this is called Standard reduction potential. Reduction potential is measured in volts (v), or millivolts (mv) and expressed as E°. The force which drive an element to acquire electrons and thereby be reduced is called Reduction potential of the element. In simple words, an electrochemical series is an arrangement of elements in terms of their ability to acquire electrons and thereby get reduced. The basic fact is ranking of oxidizing and reducing substances in terms of their strength for oxidation and reduction in a chemical reaction depends on their relative ability to gain or lose electrons.Įlectrochemical series is a tool to predict relative power of oxidizing and reducing agents. Opposite to this, the more readily a substance gains electrons, the more stronger it is as oxidizing agent. It is obvious, more readily a substance loses electrons, the more powerful it is as reducing agent. Once this basic fact is understood, every aspect of Redox process falls in line. A reducing agent is a substance which loses electrons and get oxidized. Recap - An oxidizing agent is a substance which makes other to lose electrons and gains those electrons to get reduced.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
